TCFD Disclosure
In May 2021, EIZO has announced its support for the recommendations of the TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure)*1.

Since the launch of our own brand, we have been consistently working on the most advanced environmental measures, pursuing the energy-saving performance of our products, setting targets for reducing GHG emission across all business activities, and taking other actions to combat climate change*2.
- *1 The Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
In response to a request from the G20, the Financial Stability Board (FSB) established the TCFD to examine climate-related disclosure and responses by financial institutions. TCFD encourages companies and other organizations to disclose their governance, strategy, risk management, indicators and targets with respect to climate change-related risks and opportunities. - *2 Greenhouse Gas
Kyoto Protocol defines seven types of greenhouse gases to be reduced: carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH4), dinitrogen monoxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) in the second commitment period starting in 2013.
Governance
A Sustainability Committee has been established to address issues related to climate change. In addition, the Climate Change Response Subcommittee has been established to evaluate and respond to climate-related risks and opportunities bacause of their specialized characteristics. The President & COO, who chairs the Sustainability Committee, is responsible for addressing issues related to sustainability.
The Board of Directors monitors and supervises the progress of the goals and targets for addressing climate-related issues through the formulation of strategies for realizing opportunities based on GHG emission reductions and scenario analysis by the Sustainability Committee, and through quarterly reports on the status of business execution.
Sustainability Management Structure
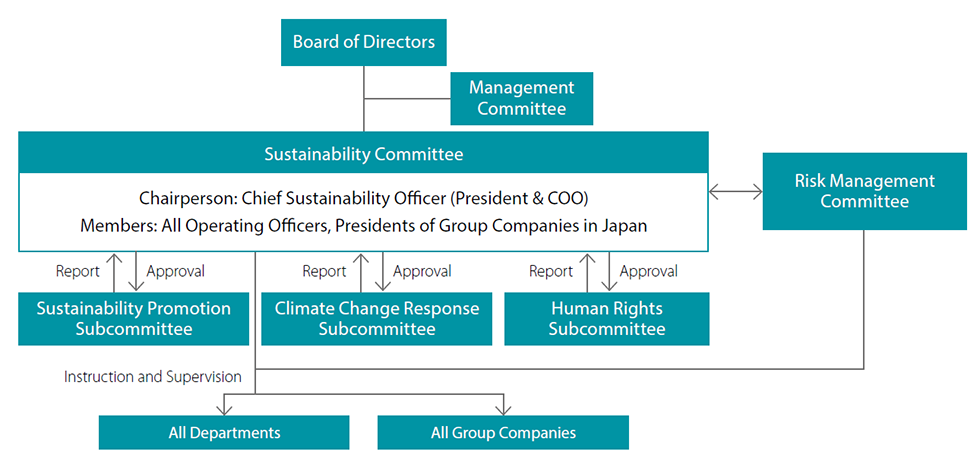
| Organization Name | Role | Members | Frequency | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Board of Directors |
|
All Directors | 4 times/Y | |
| Sustainability Committee |
|
Chairperson: Director responsible for Sustainability (President & COO) Members: All executive officers and presidents of Group companies |
4 times/Y | |
| Sustainability Management Subcommittee |
|
Selected by the Sustainability Committee Secretariat from among the members of each department and group company and appointed by the Sustainability Committee | ||
| Climate Change Response Subcommittee |
|
Same as above | ||
| Risk Management Committee |
|
Chairperson: Director responsible for Risk Management (President & COO or a person appointed by the President & COO) Members: All executive officers and presidents of Group companies |
2 times/Y | |
Risk Management
We have established and are operating a company-wide risk management system to manage risks in an integrated and unified way, recognizing that the appropriate management of risks surrounding the EIZO group is essential for achieving management goals and implementing business strategies.
Climate-related risks and opportunities are analyzed and evaluated by the Sustainability Committee and the Climate Change Response Subcommittee in order to encompass responses to long-term and specialized risks and opportunities indicated by TCFD in conjunction with company-wide risk management, and countermeasures are discussed.
Climate-Related Risk Management Process

Strategy
Scenario Analysis
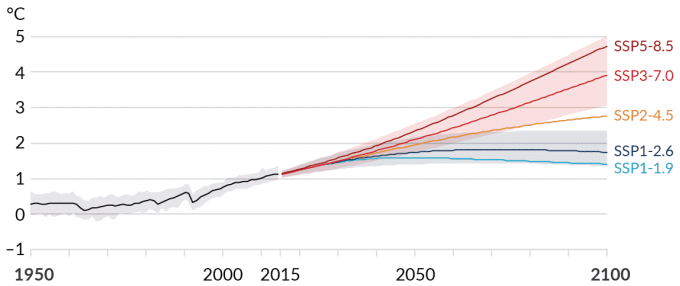
We have analyzed the scenarios recommended by the TCFD for the 2℃ scenario (SSP1-2.6) and the 4℃ scenario (SSP5-8.5) in the IPCC*3 AR6 to determine what business challenges may emerge in the highly uncertain future as we transition to a decarbonized society.
The scenario analysis covered all of our businesses, including domestic and overseas groups, and the timeframe was set in accordance with our medium to long-term strategy. When identifying materialities related to sustainability, we used the year FY2030, which is also the goal of the SDGs, as the long-term timeframe. Therefore, for climate-related risks, we also set the year FY2030 as a long-term time perspective given a highly uncertain future. These analyses take into account not only direct operations, but also the entire supply chain, including raw material procurement, and the value chain, including customers.
- *3 IPCC(Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change)
| Scenario | Reference | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 2℃Scenario |
|
The 2℃ or lower scenario is a scenario that temperature rise is well below 2℃ by 2100 due to negative real GHG emissions after 2070. SSP1-2.6 is a worldview that emphasizes the importance of national development and the achievement of sustainability goals. Also, IEA SDS is compatible with the less ambitious 2℃ goal of the Paris Agreement, which is much lower. |
| 4℃Scenario |
|
The 4℃ scenario is a scenario that temperature rise exceeds 4℃ by 2100 unless climate change actions are taken to exceed current conditions. And IEA STEPS is a worldview that does not assume all goals announced by the government will be achieved. |
- *4 SSP(Shared Socioeconomic Pathways)
- *5 IEA(International Energy Agency)
- *6 SDS(Sustainable Development Scenario)
- *7 STEPS(Stated Policies Scenario)
The IEA NZE 2050 was also referred in the analysis of the 2℃ scenario.
SSP:Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
| Scenario | Near Term, 2021-2040 | Mid-term, 2041-2060 | Long Term, 2081-2100 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best estimate(℃) | Vely likely range(℃) | Best estimate(℃) | Vely likely range(℃) | Best estimate(℃) | Vely likely range(℃) | |
| SSP1-1.9 | 1.5 | 1.2 - 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.2 – 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.0 – 1.8 |
| SSP1-2.6 | 1.5 | 1.2 - 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.3 – 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.3 - 2.4 |
| SSP2-4.5 | 1.5 | 1.2 - 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.6 – 2.5 | 2.7 | 2.1 - 3.5 |
| SSP3-7.0 | 1.5 | 1.2 - 1.8 | 2.1 | 1.7 – 2.6 | 3.6 | 2.8 – 4.6 |
| SSP5-8.5 | 1.6 | 1.3 - 1.9 | 2.4 | 1.9 – 3.0 | 4.4 | 3.3 – 5.7 |
IPCC AR6 WG1, SPM p14
Global surface temperature change relative to 1850-1900
IPCC AR6 WG1, SPM p22
Risks and Opportunities
The Sustainability Committee identified "Materiality" as a key issue for the EIZO Group.
Among them, we have come to recognize that the climate change is one of the key issues. We have also identified the following climate change-related risks and opportunities from a long-term perspective in accordance with the "Sustainability Management Basic Rules".
The criteria for assessing the materiality of the risks and opportunities are determined by considering the impact and likelihood of occurrence above a certain scale on sales and profit/loss.
| Categories | Areas | Items | Terms | Countermeasures | Impact | Scenario | EIZO’s Value Chain | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | R&D | Procurement | Production | Sales and Service | Disposal and Recycle | |||||||
| Transition Risks | Policy and Legal Risks | Increase in tax burden due to higher GHG emission price | Medium/Long |
|
Small | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● |
| Increase in manufacturing costs due to higher procurement costs | Short/Medium |
|
Big | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ||||||
| Increase in costs for introduction of renewable energy and investment in equipment for energy conservation | Short/Medium | - | Small | 2℃ | ● | |||||||
| Rising transportation costs due to a shift in general social expectations to reduce GHG emissions(Increased costs associated with low-carbon transportation in current means of transportation, not just the shift in social expectations) | Medium/Long | - | Small | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | |||||||
| Increased regulations regarding disaster preparedness and Mandatory measures for employee safety and business continuity | Medium/Long |
|
Medium | 4℃ | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ||
| Technology Risks | Failure to achieve targets in energy conservation and low-carbonization of products | Medium/Long |
|
Big | 2℃ | ● | ● | |||||
| Increased investment in R&D to achieve low-carbonization goals | Medium/Long |
|
Medium | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | |||||||
| Market Risks | Rising energy costs due to increasing share of renewable energy and rising oil prices | Medium/Long |
|
Medium | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ● | ● | ● | ● | |
| Opportunities | Products and Services Opportunities | 【B&P、HC、CW、V&S】 Sales expansion due to increased demand for products with high environmental performance |
Medium/Long |
|
Big | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ● | |||
| 【HC】 Increasing health risks associated with climate change will foster a sense of value that emphasizes health and well-being, which expand the market |
Medium/Long |
|
Big | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ● | |||||
| 【V&S】 Increasing need for products and systems that adapt to resilient social needs in an increasingly extreme climate |
Medium/Long |
|
Medium | 2℃ 4℃ |
● | ● | ● | |||||
Duration: [Near term] -3 years / [Mid-term] 3-10 years / [Long term] 10 years or more
Impact: [Big] Risk of loss and opportunity for profit: More than 1,000million yen [Medium] More than 100million yen [Small] Less than 100 million yen
Financial Impacts
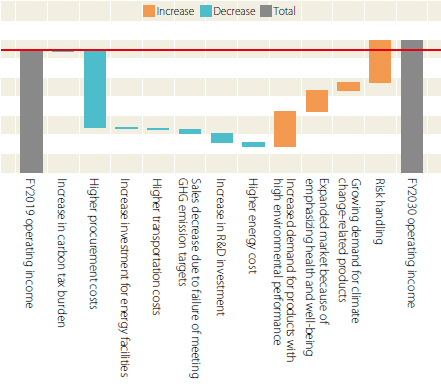
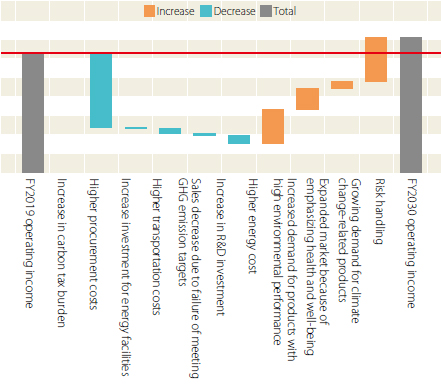
We have analyzed the specific level of financial impact in FY2030 through the 2℃ and 4℃ scenario analysis.
-
FY2030 Financial Impact under the 2°C Scenario (Comparison of Change in FY2030 Operating Income Starting from FY2019)
-
FY2030 Financial Impact under the 4°C Scenario (Comparison of Change in FY2030 Operating Income Starting from FY2019)
Under the 2℃ scenario, we assume that the financial impact of higher operating costs will be greater as a result of tighter carbon pricing policies.
Under the 4℃ scenario, the physical impacts of climate change are projected to be accompanied by logistical disruptions in our value chain and impacts on procurement costs.
At the same time, we envision that customers' product selection criteria will change as they move toward decarbonization, and that the need for more energy-efficient performance and lower GHG emissions products will increase, and that our high-efficiency products are likely to create more and more business opportunities as we move toward a low-carbon society.
Future Efforts
We are currently setting GHG emission reduction targets in accordance with SBT standards, and this scenario analysis has reaffirmed the importance of these targets: for Scope 1 and Scope 2*8 emissions, we aim for a 70% reduction by fiscal year 2030 and a 100% reduction (net zero) by fiscal year 2040, with fiscal year 2019 as the base year. In terms of Scope 3*9 emissions, we have set a target of reducing GHG emissions by 27.5% by fiscal year 2030. To achieve these reduction targets and maximize the business opportunities identified in the scenario analysis, we will work in accordance with “Transition to Net Zero”.
・Also, since reducing the carbon footprint*10 of products is an ever-increasing market need, we believe that actively promoting the development of our low-carbon products will lead to further sales growth. In order to realize a sustainable society, we have included in our Mid-Term business plan the development of environmentally friendly and sustainable products, both in the process of making our products and in the process of using them by users.
- *8 Scope 1: Direct GHG emissions that occur from sources that are controlled or owned by an organization (e.g., emissions associated with fuel combustion in boilers, furnaces, vehicles).
Scope 2: Indirect GHG emissions that occur from using electricity, heat, or steam. - *9 Scope 3: All sources not within an organization’s scope 1 and 2 boundary (purchased goods and services, upstream transportation and distribution, business travel, employee commuting, use of sold products, investments etc.)
- *10 Carbon Footprint; Total GHG emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e).
Metrics and Targets
In July 2022, our near-term science-based GHG emissions reduction targets were approved by the SBTi (Science Based Targets initiative)*11. We recognize the importance and urgency of action to combat climate change and is committed to setting ambitious emissions reduction targets in line with recent climate science with the SBTi.
Targets are considered ‘science-based’ if they are in line with what the latest climate science and the goals of the Paris Agreement.
Approved targets
- Scope1+2
(1.5℃ alignment) - Reduce absolute scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 70% by FY2030 compared to the FY2019 base year
- Scope3
(well below 2℃ alignment) - Reduce absolute scope 3 GHG by 27.5 % by FY2030 compared to the FY2019 base year
- *11 SBTi (Science Based Targets initiative): An international partnership between CDP, the United Nations Global Compact, World Resources Institute (WRI), and the Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF). It encourages companies to set science-based GHG reduction targets and reviews and validates those targets from an objective standpoint.
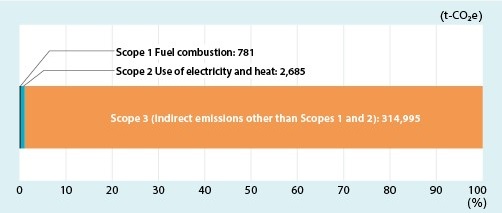
GHG emissions in Scope 1 through 3
Individual GHG emissions [t-CO₂e] in Scope1 through 3 are as follows.
| FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope 1 | 915 | 805 | 782 | 782 | 781 |
| Scope 2 | 5,531 | 4,270 | 3,120 | 3,394 | 2,685 |
| Scope 3 | 443,716 | 403,005 | 431,834 | 411,207 | 314,995 |
| Total | 450,162 | 408,080 | 435,736 | 415,383 | 318,461 |
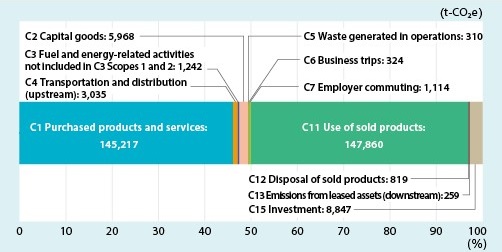
GHG Emissions by Category in Scope 3
GHG emissions [t-CO₂e] by category*12 in Scope 3 are as follows. Emissions from purchased products (Category 1) and emissions from the use of sold products (Category 11) account for 93.0% of the total emissions in Scope 3.
- *12 Category:GHG Protocol's Scope 3 criteria classify Scope 3 into 15 categories. Among them, Category1 refers to 'Purchased Goods and services' and Category11 refers to 'Use of Sold Products'.
| FY2019 | FY2020 | FY2021 | FY2022 | FY2023 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category 1 | 167,601 | 155,309 | 184,810 | 194,687 | 145,217 |
| Category 11 | 248,037 | 221,652 | 222,174 | 189,990 | 147,860 |
| Total | 415,638 | 376,961 | 406,984 | 384,677 | 293,077 |
The coverage rate for Scope 1 and 2 is 100%, and Scope 3 is over 99.7%. In the most recent year, the total of Scope 1 and 2 is reduced by approximately 46.2%.
These metrics and targets are reflected in our Mid-Term Business Plan, and we are working to achieve them.
